RockWorks | ModOps | Grid | Directional | Second-Derivative
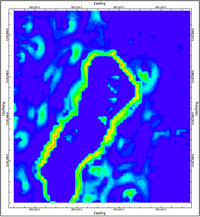
This program reads a grid (surface) model and computes the changes in Z-values (elevations, concentrations, etc.) between neighboring nodes, noting the angle and direction (0 to 360) of steepest change. It then computes the change of the slope values (the slope's slope). The resulting second derivative values are stored in a new grid model, with options for generating a 2D map and/or 3D surface. The second-derivative maps highlight areas where the slope is changing, such as where a steep wall meets a valley floor (in the above map).
Note: This program requires that a RockWorks surface model (.RwGrd file) already exist.
Menu Options
Step-by-Step Summary
- Input (Surface/Terrain) Grid: Click to browse for the name of the existing grid model (.RwGrd file) to be analyzed and displayed as a map.
- Normalize Nodes: Leave this unchecked if your grid model represents topographic elevations.
If your grid model represents something other than topography (e.g. geochemical concentrations), you should check this box so that the Z values can be normalized to map units prior to computing the slope and aspect. For example, if a grid node spacing is 10 meters and the user is analyzing geochemical data than ranges between zero and 0.01, the maximum slope would be less than one degree in which case the program would produce a blank diagram. With normalization, however, the data is now rescaled to resemble a three-dimensional cube in which the slope will have a wide range (i.e. zero to 90 degrees).
- Automatic: Using this normalization scheme, the program will rescale the grid node values such that the minimum node value will represent zero while the maximum node value will be equal to the map distance from the southwest corner to the northeast corner of the grid model. The map below illustrates a second-derivative contour map based on normalized geochemical data that initially ranged between zero and 0.01.
-

- Manual: Choose this option if you want to enter your own min and max range within which the grid node values are to be normalized before the analysis is run.
- Output Grid: Click to the right to type in the name to assign to the new grid model that will be created, with 2nd derivative computations recorded for the Z values.
- 2D Grid Map
Check this box to display the output grid as a 2D map at this time.
Click this tab to set up the 2D map layers (bitmap, symbols, labels, line contours, color-filled contours, labeled cells, map border, etc.).
- 3D Grid Diagram
Check this box to display the output grid as a 3D surface at this time.
Click this tab to set up the 3D map layers (surface colors, images, reference cage, etc.).
! You can request both a 2D and 3D representation of the grid model.
- Be sure you have a RockWorks grid model already created, for input into this program.
- Select the ModOps | Grid | Directional | Second-Derivative menu option.
- Enter the requested menu settings, described above.
- Click the Process button to continue.
The program will read the input grid model, compute the slope and aspect for each node, then compute the slope of the slope and store these second-derivative values for each node.
The requested diagram(s) will be displayed in a RockPlot2D tab and/or RockPlot3D tab in the Options window.
- You can adjust any of the settings in the Options window (input grid model name, map settings, etc.) and then click the Process button again to regenerate the map.
- View / save / manipulate / export / print the map in the RockPlot2D or RockPlot3D window.
 Back to Grid Menu Summary
Back to Grid Menu Summary

RockWare home page



![]() Back to Grid Menu Summary
Back to Grid Menu Summary