
RockWorks | Utilities | EarthApps | Points | Cylinders | Advanced
This program:
- Reads a listing of data from the Datasheet Editor: XY locations and (optionally) size declarations, measured values, colors, and label content.
- Creates a KML output file in which the point locations are represented illustrated with 3D cylinders, whose radius, height, and color are either fixed, defined in the datasheet, or scaled proportionally based on measurements in the datasheet.
- Creates a KMZ (zip) output file, containing the KML file.
- Loads the KMZ file in Google Earth.
This is the most flexible (and complicated) cylinder map option.
See also: Cylinder Maps - Simple, Cylinder Maps - Proportional
Menu Options
Step-by-Step Summary
Menu Options
- Input Columns: The prompts along the left side of the window tell RockWorks which columns in the input datasheet contain the required data.
Click on an existing name to select a different name from the drop-down list. See a sample data layout below.
- X: Column that contains the X coordinates for the points.
These can be Eastings in meters or feet, decimal longitudes, etc. See Defining your Datasheet Coordinates for more information.
- Y: Column that contains the Y coordinates for the points.
- Radii: Defines the radius of the cylinders.
- Fixed: Click in this button if all of the cylinders are to have the same radius.
- Radius (Meters): Defines the radius for all of the cylinders, in meters.
For example, an entry of 1000 would create cylinders that have a radius of 1 kilometer.
- Variable (Defined by Column): Click in this button if the radius for each cylinder is listed in the datasheet.
- Radius Column: Defines which column in the datasheet contains the radius listings and units.
Click on the current name displayed to the right, to choose a different column name from the drop-down list.
- Proportional (Scaled Relative to Data Column): Click this button to create cylinders with varying radii, scaled automatically based on any measured value in the datasheet.
- Data Column: Defines which column in the datasheet contains the measurements to use for scaling the cylinders.
Click on the current name displayed to the right, to choose a different column name from the drop-down list.
- Minimum Radius (Meters): Defines the radius for the cylinders, as expressed in meters, for the sample sites with the smallest value measurement (as read from the Data Column defined above).
For example, an entry of 1000 would create cylinders that have a radius of 1 kilometer for those sites with the minimum data value.
- Maximum Radius (Meters): Defines the radius for the cylinders, in meters, for the sample sites with the largest value measurement (as read from the Data Column defined above). Sites with intermediate Z values will be scaled proportionally between the minimum and maximum radii.
- Height: Defines the height of the cylinders.
- Fixed: Click in this button if all of the cylinders are to have the same height.
- Height (Meters): Defines the height for all of the cylinders, in meters.
For example, an entry of 10000 would create cylinders that have a height of 10 kilometers.
- Variable (Defined by Column): Click in this button if the height for each cylinder is listed in the datasheet.
- Height Column: Defines which column in the datasheet contains the height listings and units.
Click on the current name displayed to the right, to choose a different column name from the drop-down list.
- Proportional (Scaled Relative to Data Column): Click this button to create cylinders with varying heights, scaled automatically based on any measured value in the datasheet.
- Data Column: Defines which column in the datasheet contains the measurements to use for scaling the cylinders.
Click on the current name displayed to the right, to choose a different column name from the drop-down list.
- Minimum Height (Meters): Defines the height for the cylinders, as expressed in meters, for the sample sites with the smallest value measurement (as read from the Data Column defined above).
For example, an entry of 5000 would create cylinders that have a height of 5 kilometers.
- Maximum Height (Meters): Defines the height for the cylinders, in meters, for the sample sites with the largest value measurement (as read from the Data Column defined above). Sites with intermediate Z values will be scaled proportionally between the minimum and maximum heights.
- Colors: Defines the fill color for the cylinders.
- Fixed: Click in this button if all of the cylinders are to plot in the same color.
- Color: Defines the color for the cylinders. The current color is displayed to the right. To change the color, click on the color sample and choose a new color from the drop-down list.
- Variable (Defined by Column): Click in this button if the color for each cylinder is listed in the datasheet.
- Color Column: Defines which column in the datasheet contains the colors.
Click on the current name displayed to the right, to choose a different column name from the drop-down list.
- Proportional (Scaled Relative to Data Column): Click this button to create cylinders with varying colors, assigned automatically based on any measured value in the datasheet.
- Data Column: Defines which column in the datasheet contains the measurements to use for coloring the cylinders. RockWorks will assign colors using a cold-to-hot scale (cold for low values, hot for high).
Click on the current name displayed to the right, to choose a different column name from the drop-down list.
- Include Labels: Insert a check here to label the site in the Google Earth side panel and in the map.
- Label Column: Defines the column that contains the text to be used for the labels.
Click on the current name displayed to the right, to choose a different column name from the drop-down list.
- Color: Defines the color for the labels.
Click on the current color, displayed to the right, to choose a different color.
- Scale: Defines the size of the labels. Default = 1.
Rule of thumb: 0.5 will create small labels, 2.0 large labels.
Step-by-Step Summary
- Access the Utilities program tab.
- Create a new datasheet and enter or import your location coordinates, and any of the optional fields, into the datasheet.
Or, open one of the sample files and replace that data with your own. (In this example, the sample file = "RockWorks17 Data\EarthApps Samples\Cylinders_Advanced_01.rwDat")
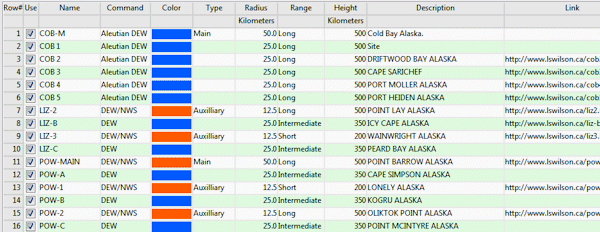
Longitude and latitude coordinates must be in decimal format. If you're using another coordinate system, be sure you've specified the Units and the Projection Settings as appropriate.
- Select theRockWorks | Utilities | EarthApps | Points | Cylinders | Advanced menu option.
- Enter the menu options as described above.
! Tip: If you're working with one of the sample .rwDat files, you can load its specific menu settings by (1) clicking on the Menu button at the top of the window, (2) clicking Load from RCL, and (3) browsing for the .rcl file with the same name as the .rwDat file you're working with.
- Click the Process button to continue.
The program will create a KML file containing a map in which the point locations are represented with filled 3D cylinders, using the scaling, coloring, and labeling options you specify. It will create a KMZ (zip) file containing the KML file. The Google Earth KML and KMZ file names will be assigned automatically.
- If RockWorks displays the KMZ name in a popup window for your reference, you can confirm:
- Automatically load file into Google Earth: Be sure this is checked if you want to display the output at this time.
- Show this message every time a KMZ File is Created: If checked, this window will be displayed each time a Google Earth output is created. Uncheck this if you prefer not to see this window in the future.
(Both of these settings are also available via the Preferences menu.)
- Click OK to continue or Cancel to cancel the operation.
The resulting map will be displayed in Google Earth, if requested.
 Back to Point Map Summary
Back to Point Map Summary
"Google" is a trademark of Google Inc.

RockWare home page



![]() Back to Point Map Summary
Back to Point Map Summary