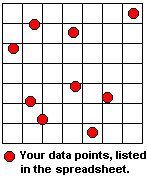
Gridding is a process in which scattered, spatially-distributed data can be transformed into a continuous array or grid of numeric values. Data to be gridded can represent anything from topographic elevations in a county to ratings of local pizza joints, as long as the original data points have location coordinates (X and Y) and a measured (numeric) "Z" value of some kind. The locations coordinates must be in a Cartesian coordinate system.
Within RockWorks, you can perform "basic" gridding of generic X,Y,Z data for 2D and 3D maps using the ModOps | Grid | Create menu. You can also create grid models of stratigraphic surfaces and aquifer surfaces in the Borehole Manager (Stratigraphy and Aquifers menus). Grid models are stored in files with an .rwGrd file name extension.
You might picture a grid model as a grid of imaginary lines that overlays your source data points.

In the process of gridding, the program assigns a value to the grid line intersections, called grid nodes.
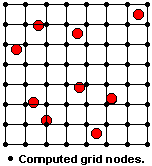
A grid file is the computer file of numbers that contains the results of the gridding process. It contains a listing of the X and Y location coordinates of the regularly-spaced grid nodes and the extrapolated Z value at each node.
The images below show scattered borehole locations and an extrapolated grid model, displayed in plan view and as a 3D surface.

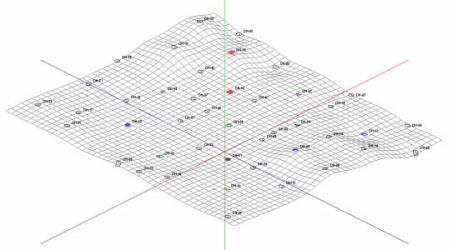
The program offers several methods to do this interpolation of your data. Each operates differently, and each has strengths and differences. See "Gridding Methods" below.
Grid files can also result from other RockWorks Grid, Volume, and Solid menu tools, and they can be imported from other software programs.