Solid modeling is a true 3-dimensional gridding process, in which a solid modeling algorithm is used to extrapolate G values for a fixed X (Easting), Y (Northing), and Z (elevation) coordinates. The G values can represent geochemical concentrations, geophysical measurements, or any other downhole or subsurface quantitative value.
The RockWorks Utilities | Solid | Model program creates solid models from X, Y, Z, and G data listed in the main datasheet or in an external text file. The Borehole Manager's Lithology, I-Data, P-Data, and Fractures menu tools (Profile, Section, Fence and Model) create solid models from lithology, i-data, p-data, or fracture data in the respective data tabs.
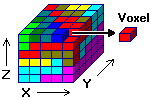
Once it knows the dimensions of your study area, the program divides it into three-dimensional cells or "voxels," their dimensions automatically or user-determined. Each voxel is defined by its corner points or node. Each node is assigned the appropriate X, Y, and Z location coordinates according to its relative placement within the study area. A fourth variable, "G", which can represent grade of ore, concentration of pollutants, etc., is estimated based on the G value of the given data points.

There are several methods offered to do this interpolation of your data. Each operates differently, and each has strengths and differences. These are discussed under Solid Modeling Methods below. Solid models are stored in files with an .RwMod file name extension.
Topics