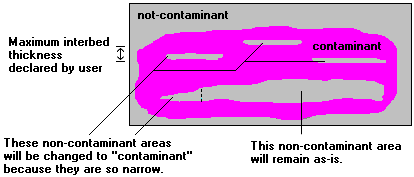
Let’s say you are computing volume of contaminated soil (solid model G value = ppm). During the computation process, the program creates a solid model of the contaminant distribution in your study area, and it creates a Boolean model of the "contaminant" and "not-contaminant" areas, based on your declared G value cutoff. If you were to cut into the model, there might be small lenses of "not-contaminant" that lie within larger areas of contiguous contaminated soil. Using this filter, you can tell the program that if a lens or interbed exists that is less than a specified thickness, it can be considered as contaminant.
The picture below shows an imaginary cross section showing non-contaminant lenses (gray) within a contaminant area (pink). Those non-contaminant interbeds (or portions of interbeds) with thickness less than the Maximum Interbed Thickness you enter can be reclassified as contaminant and included in volume calculations.
