- Default Z = Null (Undefined): Choose this item to assign null values to the nodes outside the network.
- Default Z = User Defined: Click on this item to type in the value that will be assigned to the grid nodes that lie outside the control area.
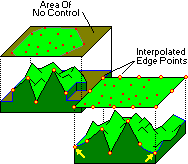
Triangulation-based gridding works like this: The data points are connected into triangles by imaginary lines, with one data point at each triangle vertex, and the triangles as close as possible to equi-angular. Once the imaginary network is determined, the slope of each triangle is computed from the three X, Y, and Z corner points. The grid nodes that lie within each triangle are assigned a z-value based on their intercept with the sloping triangular plane.
Those grid nodes that lie outside the triangle network can be assigned values using the Inverse-Distance gridding method, with a weighting exponent of "2" and quadrant searching turned off.
Advantages: This method honors the control points. Unlike the non-grid method of triangulation used in the Easy Map contouring, this method creates a data grid upon which 3D maps can be generated.
Disadvantages: Contours tend to be angular, and the process can be slow for large data sets.

![]() Back to Grid Method Summary
Back to Grid Method Summary