Inverse-Distance is one of the more common gridding methods. With this method, the value assigned to a grid node is a weighted average of either all of the data points or a number of directionally distributed neighbors. The value of each of the data points is weighted according to the inverse of its distance from the grid node, taken to a user-selected power. The greater the value of the exponent you specify, the more localized the gridding since distant points will have less influence on the value assigned to each grid node.
Advantages: The Inverse-Distance method produces a smooth and continuous grid and will not exaggerate its extrapolations beyond the given data points. The range of grid values will be smaller than the data point range: The highest grid value will be less than the maximum data point, and the lowest grid value will be greater than the minimum data point.
Disadvantages: Inverse-Distance can produce a "bulls-eye" effect in some data sets.
- Weighting Exponent: This value determines how "local" or "global" the gridding process will be. Click on this prompt to enter a real number value for the Inverse-Distance exponent. We recommend that you don’t exceed "5.0", and you should probably stick to values between "2.0" and "3.0".
- Here’s how it works: In assigning node values, the value of each data point is weighted according to the inverse of its distance (d) from the grid node, taken to the nth power, as shown here:
-
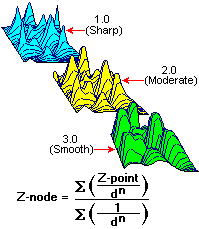
- By raising the distance factor in the denominator to a power greater than one, the values of distant data points will exert less influence than nearby points on the value assigned to the grid node. The greater the value for the exponent, the less influence these distance points will have.
- Number of Points: This setting determines the maximum number of data points that are to be used when computing the grid node value. The default number is 8; increasing the number of points will decrease bulls-eyes (concentric closed contours around control points) but slow down the gridding process.
- Sector-Based Searching: If checked, this option tells the program that instead of simply finding the nearest neighbors for the Inverse-Distance gridding, regardless of where they lie, it should look for a specific number of points in each x-degree sector around the node. The sector angle can be specified by the user. This kind of directional search can improve the interpolation of grid values that lie between data point clusters. It can also increase processing time. If this box is not checked, the program will simply use the closest control points for gridding regardless of their directional position from the node.
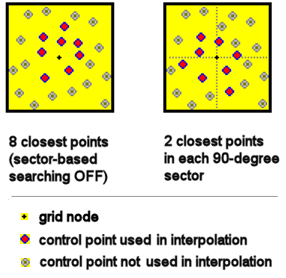
- Sector Angle: Choose the sector angle/number of sectors to use when searching for points. Example: If you choose 45 degrees (8 sectors) then the program will interpolate each grid node using the specified number of points (below) within each of the 8 sectors that lie within the cutoff distance (below) that you've defined.
- Cutoff Distance: These settings determine how far from each grid node, within each sector, the program should look for control points when assigning the node value.
- Percent: Choose this option to define the cutoff distance as a percent of the diagonal extents of the grid area. Expand this heading to enter the percent. Example, let's say your project dimensions are 1000 feet from southwest to northeast. If you set the Percent cutoff distance to "15" then for each grid node, the program will search within each defined sector for the specified number of points (below) that lie within 150 feet (0.15 * 1000) of the node.
Setting the distance as a percent can be helpful if you are working in a number of projects of different sizes, for which setting a constant distance can be problematic.
- Units: Choose this option to define the actual map units to use as the cutoff distance. Expand this heading to enter the number of units. Example: If you enter "150", then for each grid node the program would search within each sector for the specified number of points (below) within 150 feet of the node. Beware that setting defined units may cause a problem for subsequent projects with different project dimensions and data ranges.
- Points Per Sector: Click on this item to specify the number of points in each of the sectors specified above to use when interpolating the node value.
 Back to Grid Method Summary
Back to Grid Method Summary

RockWare home page


